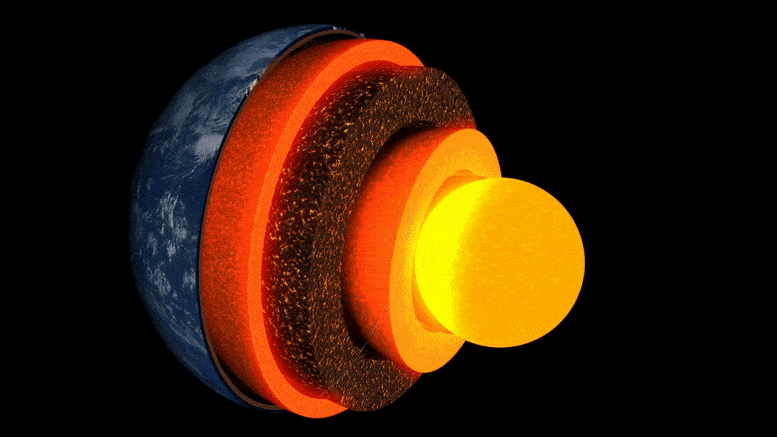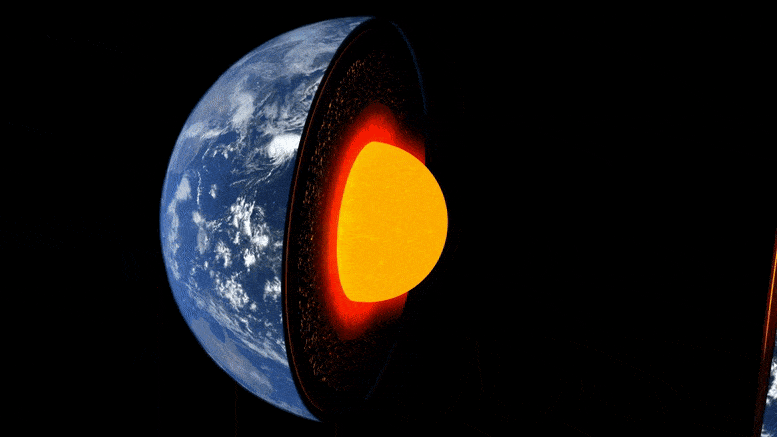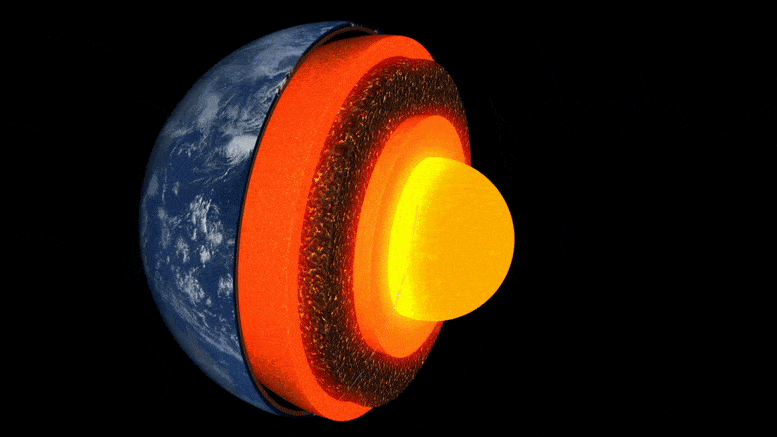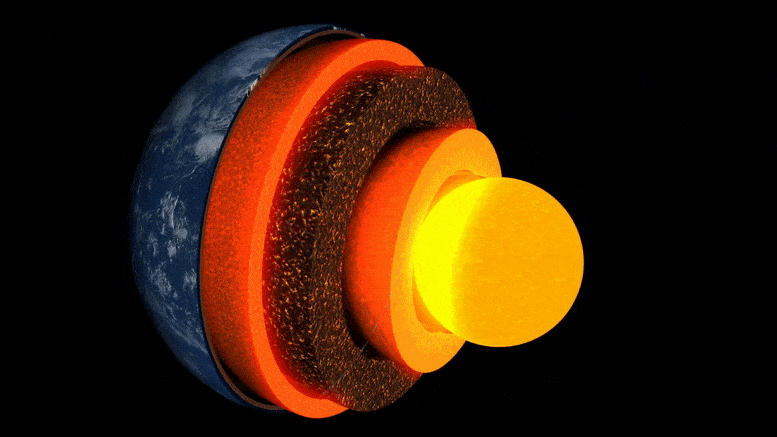
Animácia vrstiev zeme.
Nový výskum vedený univerzitou v Cambridge je prvým, ktorý získal detailný ‚obraz‘ nezvyčajného vrecka horniny v hraničnej vrstve so zemským jadrom, asi tri tisícky kilometrov pod povrchom.
Tajomná oblasť skál, ktorá sa nachádza takmer priamo pod Havajskými ostrovmi, je jednou z niekoľkých oblastí s veľmi nízkou rýchlosťou – nazýva sa tak preto, že zemetrasné vlny sa pri prechode cez ne spomalia.
Výskum uverejnený v časopise 19. mája 2022 Prírodné komunikácieje prvou, ktorá podrobne odhaľuje zložitú vnútornú asymetriu jednej z týchto enkláv, osvetľuje hlboké vnútorné krajiny Zeme a procesy v nich prebiehajúce.
„Zo všetkých najhlbších vnútorných čŕt Zeme je táto najúžasnejšia a najkomplexnejšia.“ – ako ja
„Zo všetkých hlbokých vnútorných čŕt Zeme je táto najfascinujúcejšia a najkomplexnejšia. Teraz sme získali prvý solídny dôkaz, ktorý ukazuje jej vnútornú štruktúru – je to skutočný medzník v hlbinnej seizmológii,“ povedal vedúci autor Zhi Li, doktorand. na Katedre vied o Zemi v Cambridge.
Vnútro Zeme je vytvorené ako cibuľa: v strede je železo-niklové jadro, obklopené hrubou vrstvou známou ako plášť, a nad ňou tenká vonkajšia kôra – kôra, na ktorej žijeme. Hoci je plášť pevný kameň, je dostatočne horúci, že tečie veľmi pomaly. Vnútorné konvekčné prúdy privádzajú teplo na povrch, spôsobujú pohyb tektonických platní a poháňajú sopečné erupcie.
Vedci používajú seizmické vlny zo zemetrasení, aby „videli“, čo je pod zemským povrchom – ozveny a tiene týchto vĺn odhaľujú radarové snímky hlbokého vnútra. Ale až donedávna boli „obrázky“ štruktúr na hranici jadra a plášťa, oblasti primárneho záujmu pre štúdium vnútorného tepelného toku našej planéty, zrnité a ťažko interpretovateľné.

Udalosti a trajektórie lúčov Sdiff použité v tejto štúdii. a) Prierez pretínajúci stred oblasti s ultra nízkou rýchlosťou na Havaji, zobrazujúci trajektórie lúčov pre vlny Sdiff pri 96°, 100°, 110° a 120° pre 1D PREM model Zeme. Prerušované čiary zhora nadol označujú diskontinuity 410 km, 660 km a 2 791 km (100 km nad hranicou plášťa a jadra). b) Udalosti a trajektórie lúčov Sdiff na modeli tomografu pozadia SEMUCB_WM1 v hĺbke 2791 km. Plážové lopty na podujatia natreté rôznymi farbami vrátane 20100,320 (žltá), 20111214 (zelená), 20120417 (červená), 20180910 (fialová), 20180518 (hnedá), 20181030 (ružová), 2016112 (graytriangle) staníc , a lúče. Trajektórie vĺn Sdiff v hĺbke otvoru 2791 km v spodnom plášti použitom v tejto štúdii. Udalosť použitá v krátkodobej analýze je zvýraznená žltou farbou. Navrhovaná poloha ULVZ je znázornená v čiernom kruhu. Prerušovaná čiara ukazuje prierez nakreslený v A. Kredit: Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30502-5
Výskumníci použili najmodernejšie metódy numerického modelovania na detekciu kilometrových štruktúr na hranici jadra a plášťa. Podľa spoluautora Dr. Kuangdai Lenga, ktorý vyvinul metódy, zatiaľ čo v[{“ attribute=““>University of Oxford, “We are really pushing the limits of modern high-performance computing for elastodynamic simulations, taking advantage of wave symmetries unnoticed or unused before.” Leng, who is currently based at the Science and Technology Facilities Council, says that this means they can improve the resolution of the images by an order of magnitude compared to previous work.
The researchers observed a 40% reduction in the speed of seismic waves traveling at the base of the ultra-low velocity zone beneath Hawaii. This supports existing proposals that the zone contains much more iron than the surrounding rocks – meaning it is denser and more sluggish. “It’s possible that this iron-rich material is a remnant of ancient rocks from Earth’s early history or even that iron might be leaking from the core by an unknown means,” said project lead Dr Sanne Cottaar from Cambridge Earth Sciences.

Conceptual cartoons of the Hawaiian ultra-low velocity zone (ULVZ) structure. A) ULVZ on the core–mantle boundary at the base of the Hawaiian plume (height is not to scale). B) a zoom in of the modeled ULVZ structure, showing interpreted trapped postcursor waves (note that the waves analyzed have horizontal displacement). Credit: Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30502-5
The research could also help scientists understand what sits beneath and gives rise to volcanic chains like the Hawaiian Islands. Scientists have started to notice a correlation between the location of the descriptively-named hotspot volcanoes, which include Hawaii and Iceland, and the ultra-low velocity zones at the base of the mantle. The origin of hotspot volcanoes has been debated, but the most popular theory suggests that plume-like structures bring hot mantle material all the way from the core-mantle boundary to the surface.
With images of the ultra-low velocity zone beneath Hawaii now in hand, the team can also gather rare physical evidence from what is likely the root of the plume feeding Hawaii. Their observation of dense, iron-rich rock beneath Hawaii would support surface observations. “Basalts erupting from Hawaii have anomalous isotope signatures which could either point to either an early-Earth origin or core leaking, it means some of this dense material piled up at the base must be dragged to the surface,” said Cottaar.
More of the core-mantle boundary now needs to be imaged to understand if all surface hotspots have a pocket of dense material at the base. Where and how the core-mantle boundary can be targeted does depend on where earthquakes occur, and where seismometers are installed to record the waves.
The team’s observations add to a growing body of evidence that Earth’s deep interior is just as variable as its surface. “These low-velocity zones are one of the most intricate features we see at extreme depths – if we expand our search, we are likely to see ever-increasing levels of complexity, both structural and chemical, at the core-mantle boundary,” said Li.
They now plan to apply their techniques to enhance the resolution of imaging of other pockets at the core-mantle boundary, as well as mapping new zones. Eventually, they hope to map the geological landscape across the core-mantle boundary and understand its relationship with the dynamics and evolutionary history of our planet.
Reference: “Kilometer-scale structure on the core–mantle boundary near Hawaii” by Zhi Li, Kuangdai Leng, Jennifer Jenkins and Sanne Cottaar, 19 May 2022, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30502-5

„Organizátor. Spisovateľ. Zlý kávičkár. Evanjelista všeobecného jedla. Celoživotný fanúšik piva. Podnikateľ.“